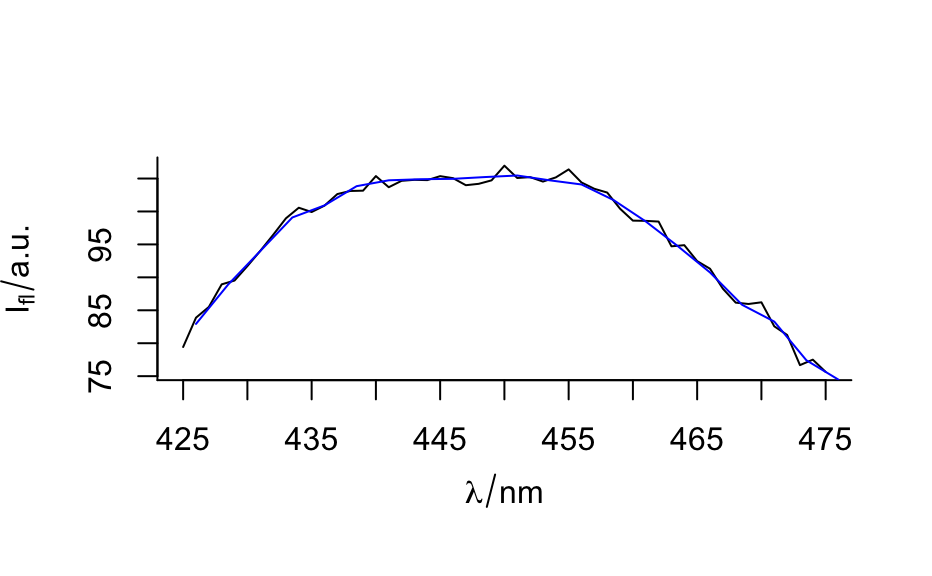
In order to reduce the spectral resolution and thus gain signal to noise ratio or to reduce the dimensionality of the spectral data set, the spectral resolution can be reduced.
spc.bin(spc, by = stop("reduction factor needed"), na.rm = TRUE, ...)
Arguments
| spc | The |
|---|---|
| by | Reduction factor. |
| na.rm | decides about the treatment of
|
| ... | Ignored. |
Value
A hyperSpec object with
ceiling(nwl(spc)/by) data points per spectrum.
Details
The mean of every by data points in the spectra is calculated.
Using na.rm = TRUE always takes about twice as long as na.rm = FALSE.
If the spectra matrix does not contain too many NAs, na.rm = 2 is
faster than na.rm = TRUE.
Author
C. Beleites
Examples
spc <- spc.bin(flu, 5)#> Warning: Last data point averages only 1 point.nwl(flu)#> [1] 181nwl(spc)#> [1] 37