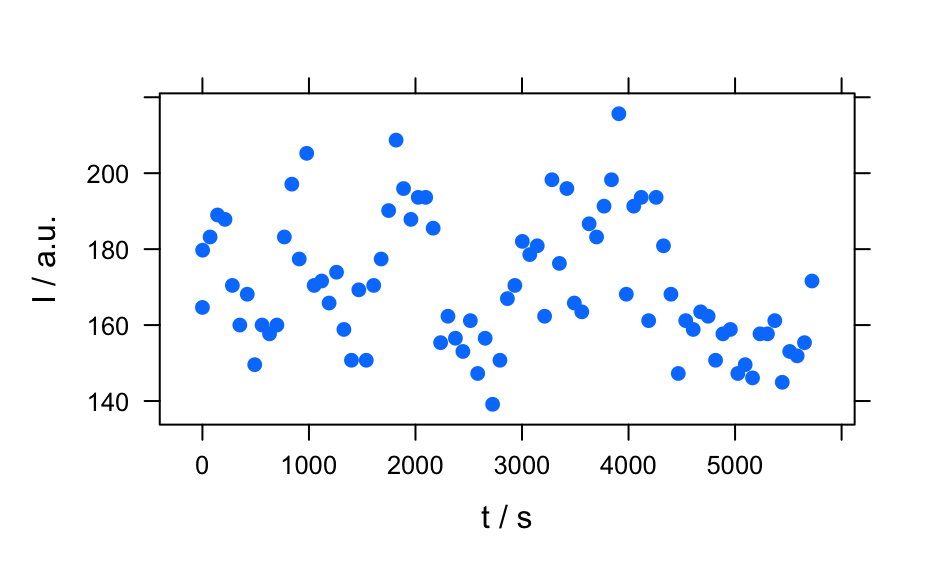The plot method for hyperSpec objects is a switchyard to plotspc(),
plotmap(), and plotc(). The function also supplies some convenient
abbreviations for frequently used plots (see 'Details').
# S4 method for hyperSpec,missing plot(x, y, ...) # S4 method for hyperSpec,character plot(x, y, ...)
Arguments
| x |
|
|---|---|
| y | String ( |
| ... | Arguments passed to the respective plot function |
Details
Supported values for y are:
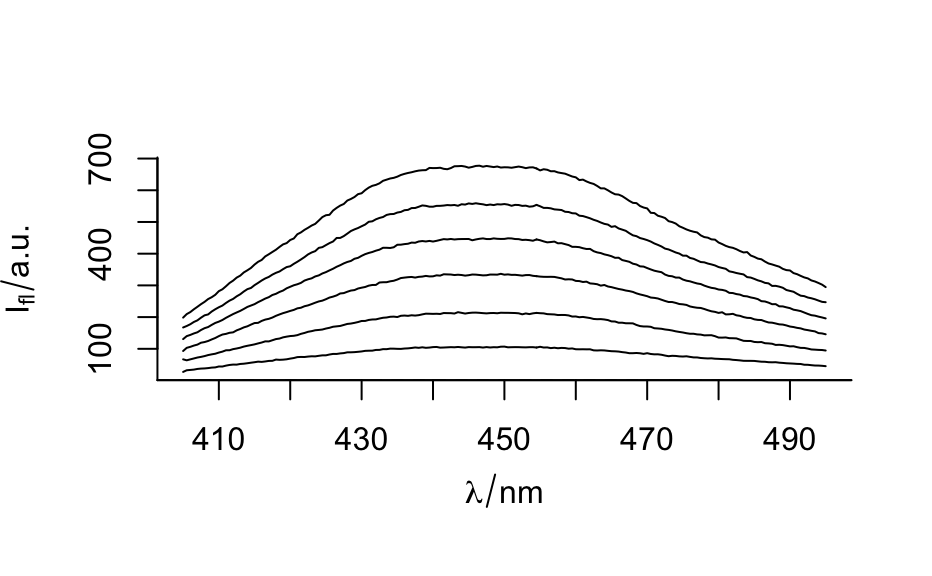
- "spc" or nothing
calls
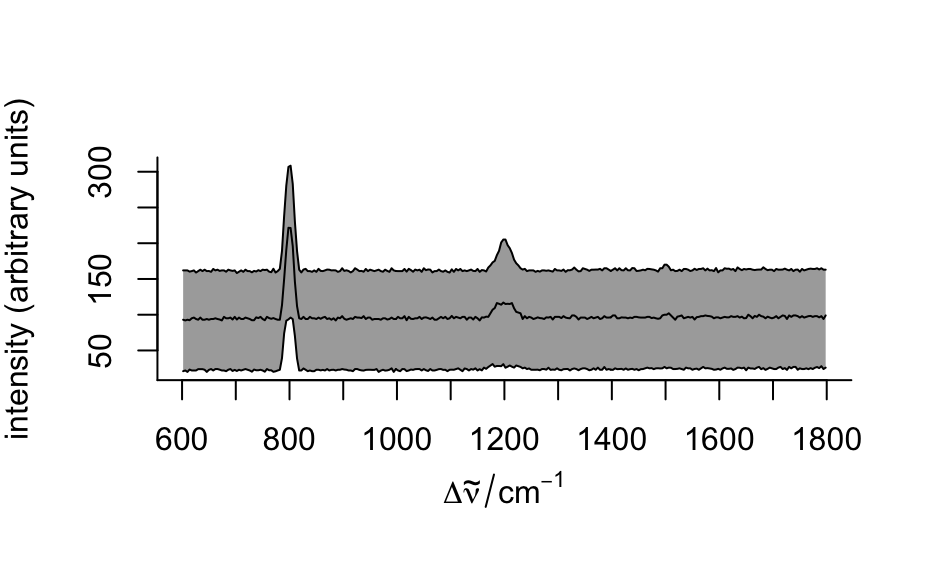
plotspc()to produce a spectra plot.- "spcmeansd"
plots mean spectrum +/- one standard deviation
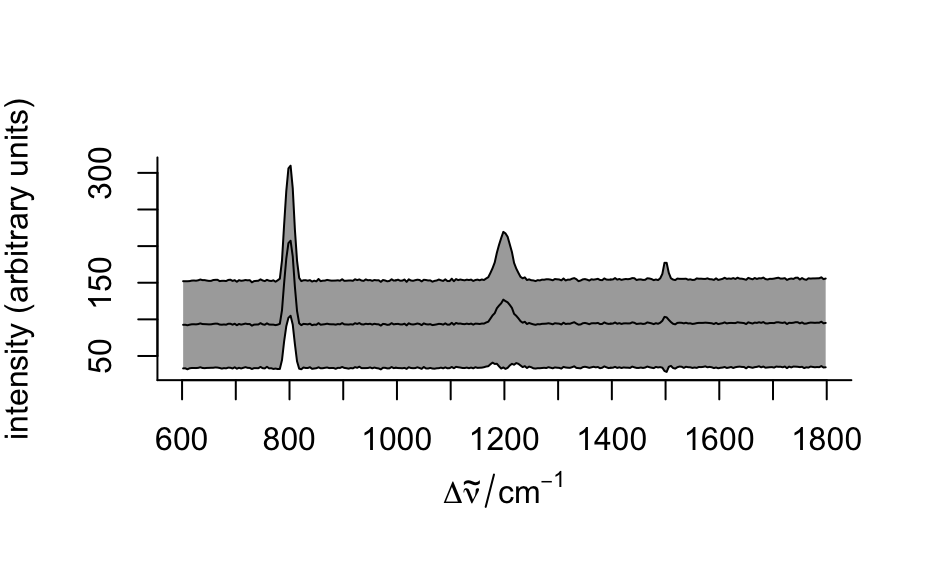
- "spcprctile"
plots 16th, 50th, and 84th percentile spectra. If the distributions of the intensities at all wavelengths were normal, this would correspond to
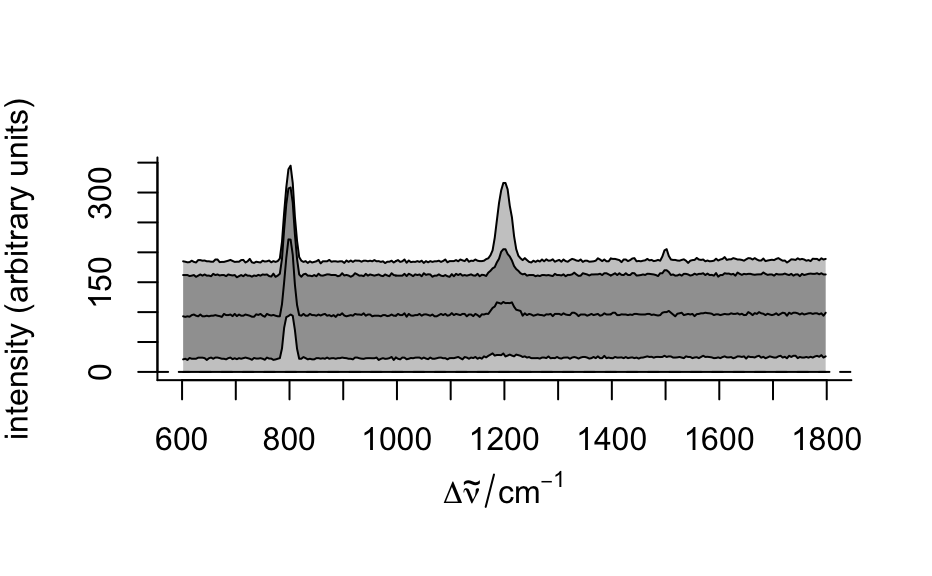
"spcmeansd". However, this is frequently not the case. Then"spcprctile"gives a better impression of the spectral data set.- "spcprctl5"
like
"spcprctile", but additionally the 5th and 95th percentile spectra are plotted.- "map"
calls
plotmap()to produce a map plot.- "voronoi"
calls
plotvoronoi()to produce a Voronoi plot (tessellated plot, like "map" for hyperSpec objects with uneven/non-rectangular grid).- "mat"
calls
plotmat()to produce a plot of the spectra matrix (not to be confused withgraphics::matplot()).- "c"
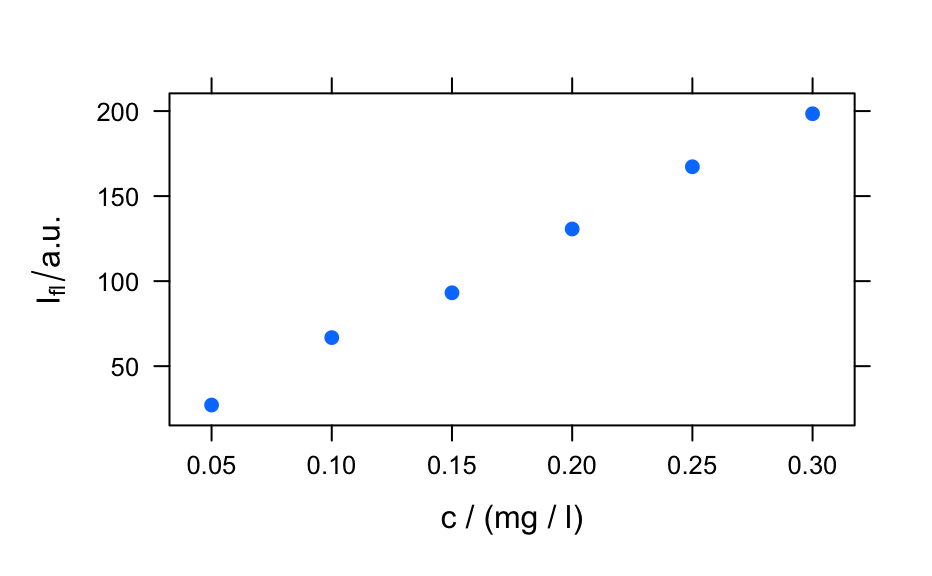
calls
plotc()to produce a calibration (or time series, depth-profile, or the like).- "ts"
plots a time series: abbreviation for
plotc(x, use.c = "t").- "depth"
plots a depth profile: abbreviation for
plotc(x, use.c = "z").
See also
plotspc() for spectra plots (intensity over wavelength),
plotmap() for plotting maps, i.e. color coded summary value on two
(usually spatial) dimensions.
Author
C. Beleites
Examples
plot(flu)plot(flu, "c")#> Warning: Intensity at first wavelengh only is used.plot(laser, "ts")#> Warning: Intensity at first wavelengh only is used.spc <- apply(faux_cell, 2, quantile, probs = 0.05) spc <- sweep(faux_cell, 2, spc, "-") plot(spc, "spcprctl5")plot(spc, "spcprctile")plot(spc, "spcmeansd")### Use plotspc() as a default plot function.